REITs vs Real Estate Investment Funds: How They Compare
Sep 27, 2024 By Rick Novak
Are you looking to diversify and invest in real estate but need clarification on the differences between a REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust) and a Real Estate Fund? This blog post will detail each type of investment's benefits, risks, and return expectations.
We'll also look at common misconceptions people have about investing in these products and how they can be used as separate yet complementary investments within your portfolio. So if you're eager to start investing in real estate without physically owning any property, read on.
REIT Definition
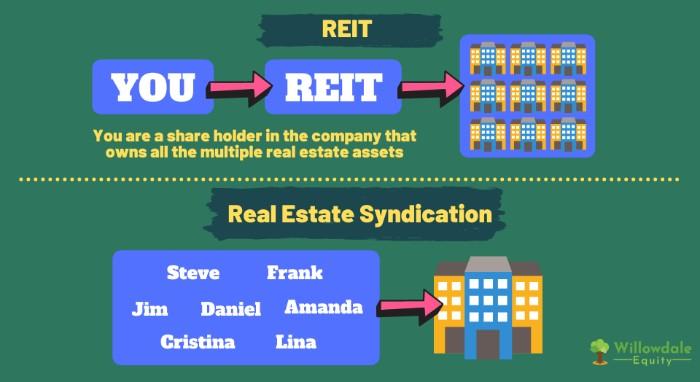
A REIT is a trust, corporation, or association that owns and invests in income-producing real estate. It pools capital from many investors to purchase, manage and finance several properties. A REIT allows you to invest in real estate without buying and managing your property. It's similar to how a mutual fund or ETF allows you to invest in a basket of stocks.
REITs typically focus on residential and commercial buildings, hotels, malls, warehouses, hospitals, and other real estate-related investments. Investing in a REIT allows you access to professionally managed real estate portfolios with the diversification of hundreds of properties in one place. The income you receive from a REIT is typically paid out quarterly as dividends.
Real Estate Fund Definition
A real estate fund is a pooled investment vehicle that invests in various real estate types, such as residential, commercial, and industrial properties. These funds allow you to invest your money with various strategies, from development to property management. Many investors turn to these funds for their access to a wider range of assets than what can be found through traditional investments.
The income you receive from a real estate fund is typically paid out quarterly as distributions, similar to the dividends of a REIT. Unlike most publically traded securities, these funds are not listed on any exchange and can be far less liquid than other investment options.
Three main types of REITs:
You should know three main REIT types: Equity, Mortgage, and Hybrid.
Equity REITs invest mainly in income-producing real estate, such as office buildings, shopping centers, apartment complexes, and other physical properties. These are the most popular REITs.
Mortgage REITs invest in and manage mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. These are generally considered the riskiest type of REITs due to the high level of leverage involved.
Hybrid REITs combine equity and Mortgage strategies, allowing investors to benefit from multiple strategies.
Three types of real estate funds
: Real estate funds come in three main varieties: open-ended, closed-end, and exchange-traded.
Open-ended real estate funds are the most common type and typically offer higher liquidity than other funds. These funds continuously raise money from investors and return it when they need it.
Closed-end real estate funds are a fixed pool of capital that does not accept new investors or return money to existing investors.
Exchange-traded real estate funds (ETFs) are similar to open-ended funds but trade on a public exchange and offer instant liquidity.
Now that we've gone over the definitions of REITs and Real Estate Funds let's look at each type of investment's benefits, risks, and returns.
Benefits of REITs and Real Estate Funds:
Diversification is one of the main benefits of investing in a REIT or real estate fund. Investing in a basket of real estate investments can mitigate the risk associated with any single property or sector.
REITs and real estate funds also tend to provide higher returns than traditional investments such as stocks and bonds. They are often seen as more attractive investments due to their income potential from rental fees and diversification benefits.
Risks of REIT vs. Real Estate Fund
As with any investment, there are always associated risks. Investing in either a REIT or real estate fund means that you're at the mercy of the market and economic conditions. The value of your investment can decrease dramatically if interest rates rise or the economy enters a recession.
Real estate funds are also typically less liquid than other investments. This means that you may have to wait a while before being able to access your money.
Returns:
The returns associated with REITs and real estate funds depend largely on the sector they're investing in and their management strategy. Depending on the fund's performance, they can range from single-digit to double-digit returns.
Additionally, by law, REITs must pay out at least 90% of their income as dividends, which can result in higher yields than traditional stocks and bonds.
It's important to note that past performance is not indicative of future returns.
Common Misconceptions:
Many people mistakenly believe that investing in a REIT or real estate fund is the same as buying an individual property. However, these investments are quite different. Investing in either of these products allows you to access professionally managed real estate portfolios with the diversification of hundreds of properties all in one investment.
Another common misconception is that investing in either of these products requires a large sum of money. While some funds may have minimum investments, many smaller funds and REITs are open to investors with limited capital.
Real estate fund structure
Before investing in a real estate fund, it's important to understand the structure of the fund and its objectives. Most funds are structured as limited partnerships or LLCs, so investors receive limited liability protection.
The fund manager typically has discretion over allocating assets and investments. Funds may invest in different real estate types, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties.
FAQs
What is a REIT?
A Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is a type of investment that pools money from many investors to purchase and manage real estate properties. With a REIT, you benefit from the managers' collective buying power and expertise while enjoying greater diversification at a lower cost than if you tried to buy and manage properties.
What is a Real Estate Fund?
A real estate fund is a pooled investment vehicle, similar to an index fund or mutual fund, that buys and sells real estate holdings on behalf of investors. These funds are managed by professional investors who use sophisticated strategies to select properties and maximize returns for their investors. Unlike REITs, these funds are actively managed and require a more hands-on approach to investing.
What are the advantages of investing in REITs and Real Estate Funds?
REITs and real estate funds offer investors access to real estate investments without having to own any property physically. They also provide diversification, offering exposure to a wide range of real estate holdings.
Are REITs better than mutual funds?
It depends on the individual investor's goals and risk tolerance. REITs offer access to real estate investments without owning property, whereas mutual funds provide a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds. Each type of investment has its advantages and risks, so investors need to understand their options before making an informed decision.
Are there any risks to investing in REITs and Real Estate Funds?
As with all investments, there are associated risks. With REITs, the risk comes from changes in the real estate market, while with real estate funds, it is due to the fund manager's strategy. Investors must research and understand the risks associated with each type of investment before making an informed decision.
What kind of return can I expect from investing in REITs and Real Estate Funds?
Returns vary depending on the type of investment, market conditions, and other factors. Generally speaking, real estate investments tend to perform better than stocks or bonds in the long term, but there is no guarantee of future performance.
Conclusion
By understanding the differences between REITs and Real Estate Funds, investors can make more informed decisions and achieve their real estate investment goals. With careful research, diversification, and knowledge of risk management strategies, investors can maximize their returns while minimizing the risks associated with each type of investment.

What is a Like-Kind Exchange

What are Top Personal Loans for Excellent Credit

A Comprehensive Review of Capital One Walmart Rewards Mastercard

What Is an After-Tax Contribution?

What Is a Covenant-Lite Loan?

Impact of Recoverable Depreciation on Financial Statements

REITs vs Real Estate Investment Funds: How They Compare

What Is Debt Signaling?
What Are Unrealized Gains and Losses?

